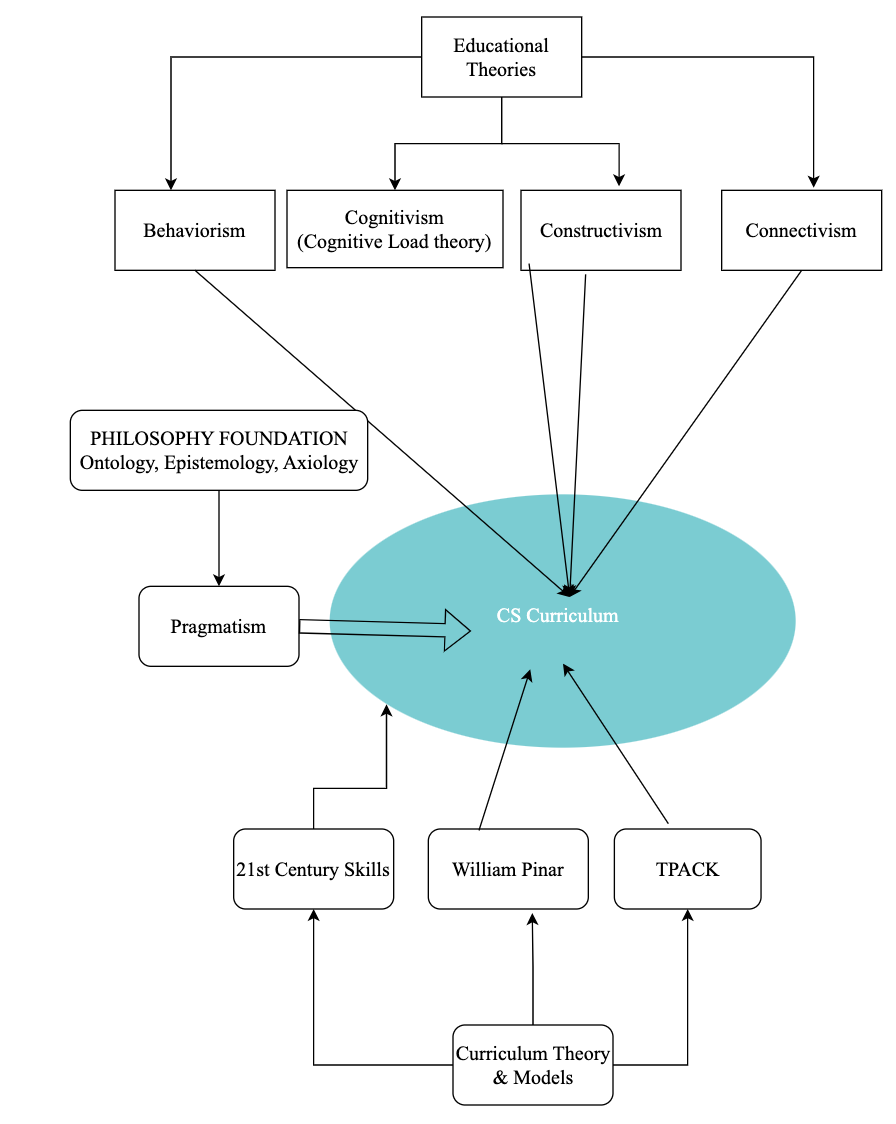
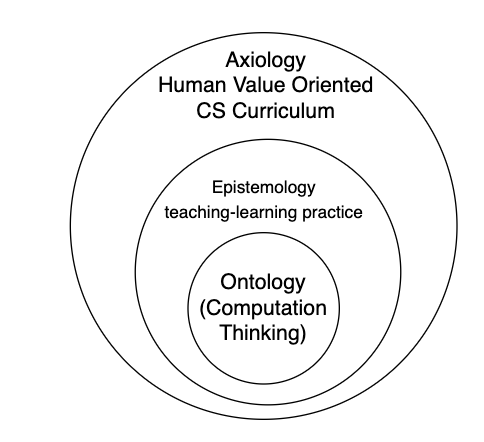
Computer Science Curriculum Development Model
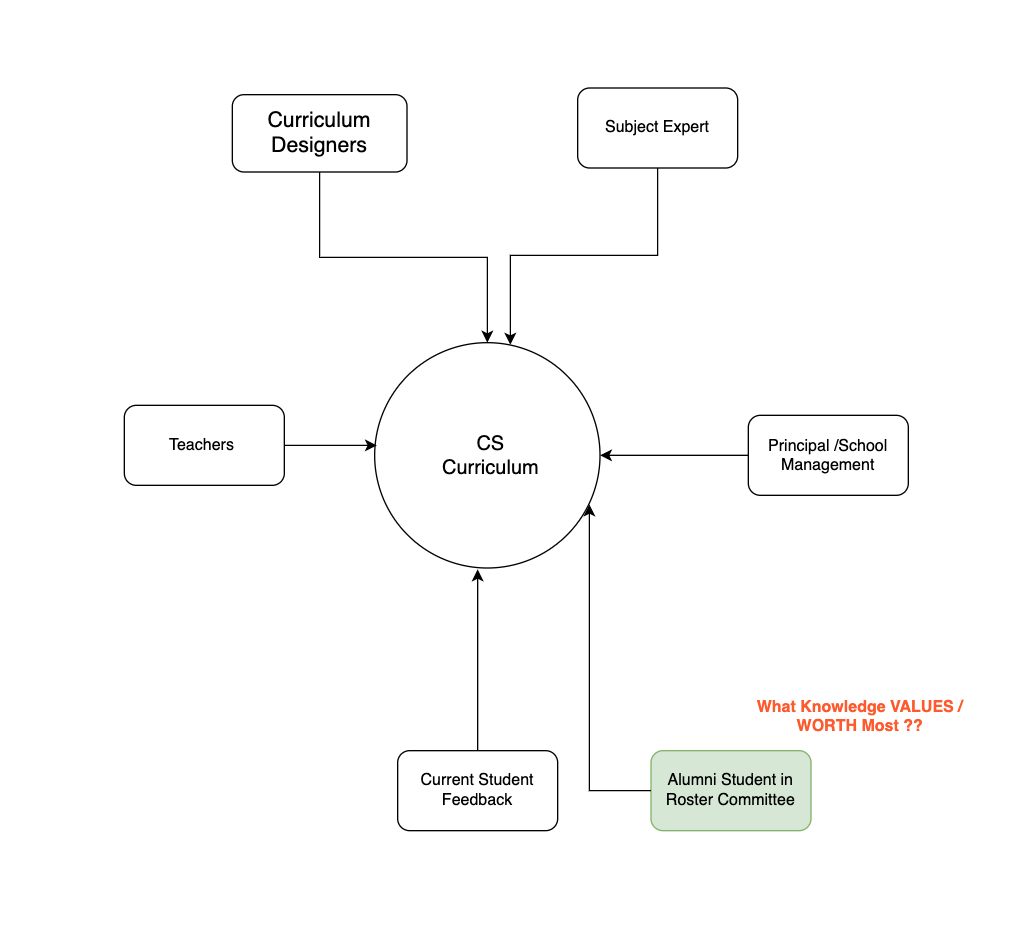
This Model is a guide map tool for developing the Student-Centric Computer Science curriculum at Secondary School Level (grades 9 to 12).
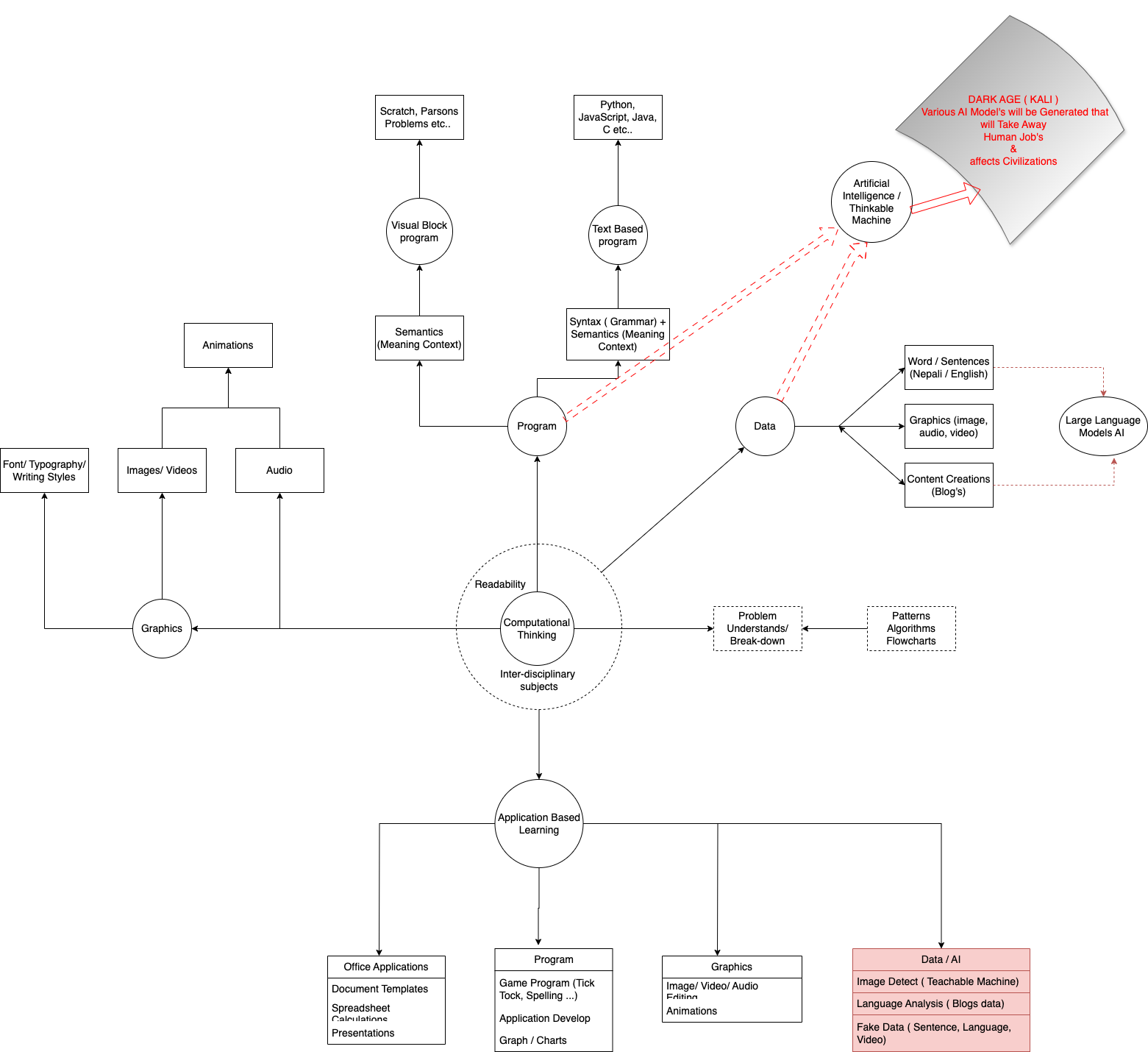
Computational thinking is the core source of Computer Science discipline. The objective
of computational
thinking is to solve problems in an algorithmic way. Computation thinking is required to be taught in an
unplugged programming way which does not require a physical Computer device.
As Computer Science is a technological advancement subject, thus the curriculum is required
to include
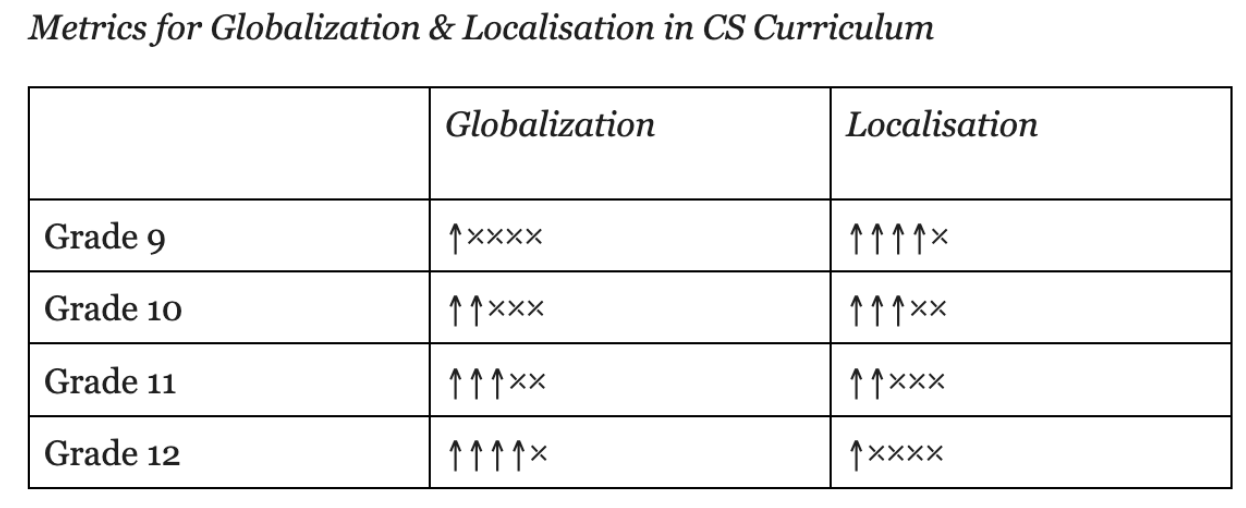
examples from interdisciplinary horizontal and vertical subjects. The Flesch-Kincaid readability tool helps to
judge the language of a textbook as per grade standard. The curriculum designers can use several readability
tools within their social context that help to standardize the textbook as per student ability.
The learning should be exploratory based on student individual interest ability. The
student interested in
drawing arts can choose graphics areas, and block based programming to explore CS concepts. Similarly,
students interested in Mathematics and problem solving can explore the text-based Programming areas. The
students interested in content creations can explore data areas. Artificial Intelligence tools are widely used
that consume the data generated by users. Various AI models are used to solve the problem specific tasks.
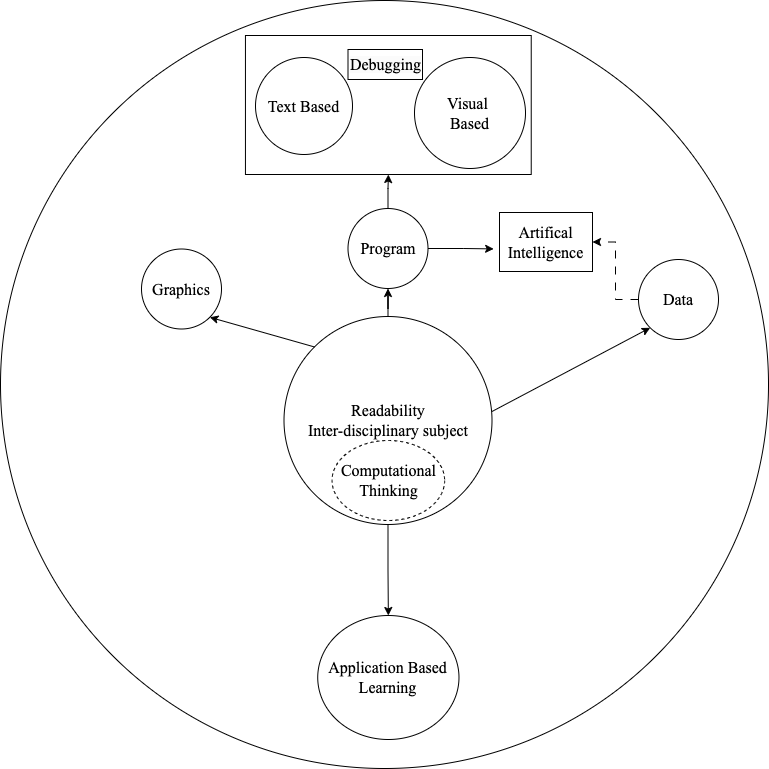
Expanded Form of the Curriculum Development Model